Hello, I’m Ed. If you’ve ever watched an elderly loved one struggle with weak legs and wondered, “What causes weak legs in the elderly?” you’re in the right place. At Elderly Independence, my mission is to explore and understand the complexities of aging and offer support for those who care for their elderly family members.
Weak legs in the elderly can be alarming and confusing. It’s a symptom that may not only limit mobility but also impacts the quality of life. As someone passionate about elderly care, I will guide you through the potential underlying causes, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors that contribute to this issue. Let’s unravel the mystery together, providing the understanding and care that our loved ones need.
Understanding what causes weak legs in the elderly is a multifaceted challenge. It requires recognizing underlying health conditions, assessing lifestyle factors, and considering the unique physiological changes that aging brings. I hope this article has illuminated the path for you, offering actionable insights and compassionate guidance.
Here at Elderly Independence, I’m committed to sharing expert-backed, research-driven content that resonates with families and caregivers. Your concerns and experiences fuel my determination to offer practical advice and empathetic understanding.
If weak legs have become a concern for an elderly person in your life, remember, you’re not alone. Professional healthcare providers and a community of support are available to assist you. Together, we can empower our elderly loved ones to live with dignity, independence, and joy, appreciating every stage of life’s journey. If you found this article helpful, feel free to explore other related topics on my website, where I strive to be a guiding light in the beautiful yet complex world of aging.
Weak legs in the elderly can significantly impact their mobility and overall quality of life. It is a common issue that can be caused by various factors, including medical conditions, age-related changes, lifestyle choices, and more. Understanding the underlying causes of weak legs is crucial in order to provide appropriate treatment and support for older individuals experiencing this problem.
Certain medical conditions can also cause weak legs in the elderly. For example, arthritis can cause joint pain and inflammation, making it difficult for older individuals to bear weight on their legs. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, can increase the risk of fractures and subsequently weaken the legs. Other medical conditions that may contribute to weak legs include peripheral artery disease, diabetes, and muscle disorders.
In conclusion, weak legs in the elderly can be caused by a combination of medical conditions, age-related factors, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these underlying causes is essential in order to provide appropriate treatment and support for older individuals experiencing this issue. By addressing the specific factors contributing to weak legs, healthcare professionals can help improve mobility and overall quality of life for the elderly population. Additionally, promoting regular exercise, a healthy diet, and other lifestyle modifications can help prevent or manage weak legs in older individuals.
What Causes Weak Legs In The Elderly: Medical conditions causing weak legs in the elderly

As individuals age, they become more susceptible to various medical conditions that can contribute to weak legs. These conditions can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact an elderly person’s mobility and overall quality of life.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD
One common medical condition that can cause weak legs in the elderly is peripheral artery disease (PAD). PAD occurs when there is a buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the legs. This lack of blood flow can result in muscle weakness and fatigue, making it difficult for older individuals to walk or perform daily activities.
Osteoarthritis
Another medical condition that can cause weak legs is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the knees and hips. The deterioration of the joint cartilage can lead to pain, stiffness, and weakness in the legs, making it challenging for the elderly to bear weight and move around.
Decrease In Bone Density
Additionally, conditions such as osteoporosis and fractures can also contribute to weak legs in the elderly. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by a decrease in bone density, making bones more prone to fractures. Fractures, especially in the hips or legs, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to walk and may result in muscle weakness.
Neurological Disorders
Furthermore, neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis can cause weak legs in the elderly. These conditions affect the nervous system and can lead to muscle stiffness, tremors, and difficulty with coordination and balance. As a result, older individuals may experience weakness in their legs and have difficulty walking or maintaining stability.
Other Conditions
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of medical conditions that can cause weak legs in the elderly. Other conditions such as diabetes, stroke, and certain types of cancer can also contribute to leg weakness. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to conduct a thorough evaluation and diagnosis to determine the underlying cause of weak legs in older individuals.
In conclusion, weak legs in the elderly can be caused by various medical conditions. Peripheral artery disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, fractures, and neurological disorders are just a few examples of conditions that can contribute to leg weakness. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for developing appropriate treatment plans and interventions to improve mobility and overall well-being in older individuals.
Age-related factors contributing to weak legs

As individuals age, there are several age-related factors that can contribute to weak legs in the elderly. These factors can include changes in muscle mass, bone density, and overall physical fitness.
Natural Loss Of Muscle Mass
One of the main age-related factors that can lead to weak legs is the natural loss of muscle mass, known as sarcopenia. As people age, they tend to lose muscle mass at a faster rate than they can build it. This can result in weakened leg muscles, making it more difficult for older individuals to maintain their balance and perform daily activities such as walking or climbing stairs.
Loss Of Bone Density
Another age-related factor that can contribute to weak legs is the loss of bone density, known as osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by the weakening of bones, making them more prone to fractures. Weak bones can affect the strength and stability of the legs, leading to weakness and difficulty in walking or standing for extended periods.
Additionally, as individuals age, their overall physical fitness levels may decline. Lack of regular exercise and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to muscle weakness and decreased leg strength. Older individuals who do not engage in regular physical activity may experience muscle atrophy and reduced muscle tone, leading to weak legs.
Furthermore, age-related changes in the nervous system can also contribute to weak legs in the elderly. Nerve damage or degeneration can affect the communication between the brain and the muscles, leading to muscle weakness and coordination difficulties.
It is important to note that while these age-related factors can contribute to weak legs in the elderly, they are not inevitable. Regular exercise, including strength training and balance exercises, can help maintain muscle mass and improve leg strength. A healthy diet rich in nutrients, particularly calcium and vitamin D, can also support bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
In conclusion, weak legs in the elderly can be caused by various age-related factors, including muscle loss, decreased bone density, reduced physical fitness, and changes in the nervous system. However, with proper lifestyle choices, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, it is possible to mitigate these factors and maintain strong and healthy legs in older age.
Lifestyle choices and weak legs in the elderly

As we age, our lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on our overall health, including the strength of our legs. Certain lifestyle choices can contribute to weak legs in the elderly population.
Sedentary Lifestyle
One of the main lifestyle factors that can lead to weak legs is a sedentary lifestyle. Lack of physical activity can cause muscles to weaken and atrophy over time. When we don’t use our leg muscles regularly, they become weaker and less able to support our body weight. This can make it difficult for older individuals to walk, climb stairs, or perform other daily activities that require leg strength.
Poor Nutrition
Another lifestyle choice that can contribute to weak legs is poor nutrition. A diet lacking in essential nutrients, such as protein, calcium, and vitamin D, can weaken muscles and bones. Without proper nutrition, the muscles in the legs may not receive the necessary nutrients to maintain their strength and function.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Additionally, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to weak legs in the elderly. Smoking reduces blood flow to the muscles, which can lead to muscle weakness. Excessive alcohol consumption can also have a negative impact on muscle health and strength.
Furthermore, obesity can put extra strain on the legs and lead to weakness. Carrying excess weight can make it more difficult for the leg muscles to support the body, leading to muscle fatigue and weakness over time.
Environmental Factors
Lastly, certain environmental factors, such as living in a home with multiple levels and no elevator, can contribute to weak legs in the elderly. Constantly climbing stairs without proper support or assistance can put a strain on the leg muscles and lead to weakness.
In conclusion, lifestyle choices play a significant role in the development of weak legs in the elderly. A sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and environmental factors can all contribute to muscle weakness in the legs. It is important for older individuals to engage in regular physical activity, maintain a healthy diet, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, manage their weight, and create a safe and supportive living environment to prevent or improve weak legs.
The role of muscle loss in weak legs
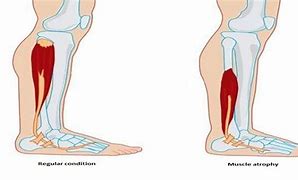
Muscle loss, also known as sarcopenia, is a common age-related condition that can contribute to weak legs in the elderly. As people age, they naturally experience a decline in muscle mass and strength. This can be exacerbated by factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions.
Decrease In Physical Activity
One of the main reasons muscle loss occurs in older individuals is due to a decrease in physical activity. Many elderly individuals become less active as they age, leading to muscle atrophy and weakness. Additionally, a lack of exercise can also lead to decreased blood flow to the muscles, further contributing to muscle loss.
Poor Nutrition
Another factor that can contribute to muscle loss in the elderly is poor nutrition. As people age, their bodies may have difficulty absorbing and utilizing nutrients, leading to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. These nutrients are crucial for maintaining muscle mass and strength. Without an adequate intake of protein, for example, the body may not have the necessary building blocks to repair and build muscle tissue.
Chronic Diseases
Certain medical conditions can also contribute to muscle loss and weak legs in the elderly. Chronic diseases such as diabetes, kidney disease, and cancer can all affect muscle health. Additionally, hormonal imbalances, such as a decrease in testosterone levels in men, can also contribute to muscle loss.
It is important to address muscle loss in the elderly as weak legs can significantly impact their mobility and independence. Regular exercise, particularly strength training exercises, can help slow down the progression of muscle loss and improve leg strength. A balanced diet that includes an adequate amount of protein and other essential nutrients is also crucial for maintaining muscle mass.
In conclusion, muscle loss plays a significant role in weak legs in the elderly. Factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions can contribute to muscle atrophy and weakness. Addressing muscle loss through regular exercise and a balanced diet is essential for maintaining leg strength and overall mobility in older individuals.
Neurological disorders and weak legs in the elderly
Neurological disorders can be a significant cause of weak legs in the elderly population. These disorders affect the nervous system, which plays a crucial role in controlling muscle movement and strength. As individuals age, their nervous system may become more susceptible to damage and dysfunction, leading to weakness in the legs.
Peripheral Neuropathy
One common neurological disorder that can cause weak legs is peripheral neuropathy. This condition occurs when there is damage to the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. Peripheral neuropathy can result from various factors, including diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, and certain medications. The damage to the nerves can lead to muscle weakness, numbness, and pain in the legs.
Parkinson’s Disease.
Another neurological disorder that can contribute to weak legs is Parkinson’s disease. This progressive disorder affects the brain’s ability to produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate movement. As Parkinson’s disease progresses, individuals may experience muscle stiffness, tremors, and difficulty with balance and coordination, leading to weakness in the legs.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is another neurological condition that can cause weak legs in the elderly. MS is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to inflammation and damage to the protective covering of nerve fibers. This damage disrupts the normal flow of electrical impulses, resulting in muscle weakness, fatigue, and difficulty with coordination.
Other Neurological Disorders
Other neurological disorders, such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, and certain brain tumors, can also contribute to weak legs in the elderly. These conditions can cause damage to the nerves or disrupt the communication between the brain and the muscles, leading to weakness and loss of function in the legs.
It is important for healthcare professionals to properly diagnose and manage these neurological disorders to help alleviate the symptoms of weak legs in the elderly. Treatment options may include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to improve overall leg strength and function.
In conclusion, neurological disorders can be a significant cause of weak legs in the elderly population. Conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and others can lead to muscle weakness and loss of function in the legs. Proper diagnosis and management of these disorders are essential in improving leg strength and overall quality of life for older individuals.
Medications and weak legs in older individuals
Medications can play a significant role in causing weak legs in the elderly population. As individuals age, they often develop various health conditions that require medication management. Unfortunately, some of these medications can have side effects that affect muscle strength and contribute to weakness in the legs.
Statins
One common type of medication that can cause weak legs is known as statins. Statins are commonly prescribed to manage high cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. While they are effective in their intended purpose, they can also lead to muscle weakness and fatigue, including weakness in the legs. This can make it difficult for older individuals to perform daily activities and maintain their mobility.
Diuretics
Another class of medications that can contribute to weak legs is diuretics. Diuretics are often prescribed to manage conditions such as high blood pressure and heart failure. These medications work by increasing urine production and reducing fluid buildup in the body. However, they can also lead to electrolyte imbalances, including low levels of potassium and magnesium. These imbalances can cause muscle weakness, including weakness in the legs.
Opioids
Additionally, certain medications used to manage pain, such as opioids, can also contribute to weak legs in the elderly. Opioids are powerful pain relievers that can have sedating effects on the body. This sedation can lead to decreased muscle strength and coordination, making it difficult for older individuals to maintain their balance and walk properly.
It is important for healthcare professionals to carefully consider the potential side effects of medications when prescribing them to older individuals. They should weigh the benefits of the medication against the potential risks, including the impact on muscle strength and leg weakness. In some cases, alternative medications or dosage adjustments may be necessary to minimize these side effects.
In conclusion, medications can be a significant factor in causing weak legs in the elderly population. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be aware of the potential side effects of medications and to monitor their patients closely for any signs of muscle weakness or leg problems. By carefully managing medication regimens, healthcare providers can help minimize the risk of weak legs and maintain the mobility and independence of older individuals.
The impact of poor circulation on leg strength
Poor circulation can have a significant impact on leg strength in the elderly population. As individuals age, their blood vessels may become narrower and less elastic, leading to reduced blood flow to the legs. This can result in weakened muscles and decreased leg strength.
Peripheral Artery Disease
One of the main causes of poor circulation in the elderly is a condition called peripheral artery disease (PAD). PAD occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the legs become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. This can lead to pain, cramping, and weakness in the legs, especially during physical activity.
Diabetes
Another condition that can contribute to poor circulation and weak legs is diabetes. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the legs, leading to reduced blood flow and muscle weakness. Additionally, individuals with diabetes may also experience peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs and feet.
In addition to medical conditions, certain lifestyle choices can also contribute to poor circulation and weak legs in the elderly. Smoking, for example, can constrict blood vessels and decrease blood flow to the legs. Sedentary behavior and a lack of physical activity can also contribute to poor circulation and muscle weakness.
To improve circulation and strengthen the legs, it is important for elderly individuals to engage in regular exercise. Exercise helps to improve blood flow, strengthen muscles, and maintain overall leg strength. Simple activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial for improving circulation and leg strength.
In conclusion, poor circulation can have a significant impact on leg strength in the elderly population. Medical conditions such as peripheral artery disease and diabetes, as well as lifestyle choices like smoking and sedentary behavior, can contribute to reduced blood flow and muscle weakness in the legs. Engaging in regular exercise is crucial for improving circulation and maintaining leg strength in older individuals.
The importance of exercise in preventing weak legs

Regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle strength and preventing weak legs in the elderly. As individuals age, they naturally experience a decline in muscle mass and strength, known as sarcopenia. This can lead to weakness in the legs and an increased risk of falls and mobility issues.
Engaging In Physical Activity
Engaging in physical activity can help counteract the effects of sarcopenia and improve leg strength. Exercise programs that focus on strength training, balance exercises, and cardiovascular activities can all contribute to stronger legs and overall physical fitness.
Strength Training Exercise
Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance band workouts, are particularly effective in building muscle mass and strength. These exercises target the major muscle groups in the legs, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. By regularly challenging these muscles, older individuals can maintain or even increase their leg strength.
Balance Exercises
Balance exercises are also important for preventing weak legs and reducing the risk of falls. Activities like tai chi or yoga can improve balance, stability, and coordination, which are essential for maintaining proper leg function. These exercises help older individuals develop better control over their movements and reduce the likelihood of tripping or stumbling.
Cardiovascular Activities
In addition to strength and balance exercises, cardiovascular activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve overall leg strength and endurance. These exercises promote blood flow to the legs, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the muscles. Regular cardiovascular exercise can also help maintain healthy blood vessels and prevent conditions like peripheral artery disease, which can contribute to weak legs.
It is important for older individuals to consult with their healthcare provider before starting any exercise program. They can provide guidance on the most appropriate exercises based on individual health conditions and limitations. Additionally, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise to avoid injury.
In conclusion, regular exercise is crucial for preventing weak legs in the elderly. Strength training, balance exercises, and cardiovascular activities all play a role in maintaining muscle strength, improving balance, and promoting overall leg health. By incorporating these exercises into their routine, older individuals can reduce the risk of falls, maintain independence, and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the elderly regain leg strength?
Yes, many elderly individuals can regain leg strength. Through proper physical therapy, exercise, and nutritional support, it’s possible to enhance muscle function and improve overall leg strength. Tailored exercises focusing on flexibility, balance, and muscle-building, under the guidance of healthcare professionals, can lead to significant improvements.
When should I be concerned about leg weakness?
You should be concerned about leg weakness if it’s persistent, sudden, or accompanied by other symptoms. If leg weakness interferes with daily activities, causes falls, or comes along with pain, numbness, or other neurological symptoms, it may indicate a serious underlying health issue. Seeking medical advice in these situations is vital to determine the root cause and ensure appropriate care and treatment.
What causes older people to lose strength in their legs?
Older people may lose strength in their legs due to a combination of factors. These can include: Aging Muscles: Muscles tend to lose mass and flexibility with age.
Chronic Medical Conditions: Such as arthritis, peripheral artery disease, or neurological disorders.
Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise can lead to muscle atrophy.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients can affect muscle health.
Medication Side Effects: Some medicines may lead to muscle weakness.
What does weakness in the legs indicate?
Weakness in the legs can be a sign of various underlying issues, ranging from minor to serious. It may indicate: Muscle Fatigue or Strain: Often temporary and linked to overuse or lack of exercise.
Chronic Health Conditions: Such as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or Parkinson’s disease.
Nerve Damage: Including peripheral neuropathy.
Infections: Certain infections can affect nerve or muscle function.
Blood Flow Issues: Such as peripheral artery disease.
Other Places For You To Explore
Explore
Conclusion
Understanding what causes weak legs in the elderly is a multifaceted challenge. It requires recognizing underlying health conditions, assessing lifestyle factors, and considering the unique physiological changes that aging brings. I hope this article has illuminated the path for you, offering actionable insights and compassionate guidance.
Here at Elderly Independence, I’m committed to sharing expert-backed, research-driven content that resonates with families and caregivers. Your concerns and experiences fuel my determination to offer practical advice and empathetic understanding.
If weak legs have become a concern for an elderly person in your life, remember, you’re not alone. Professional healthcare providers and a community of support are available to assist you. Together, we can empower our elderly loved ones to live with dignity, independence, and joy, appreciating every stage of life’s journey. If you found this article helpful, feel free to explore other related topics on my website, where I strive to be a guiding light in the beautiful yet complex world of aging.






