Hi there, it’s Ed from Elderly Independence. Today, we’re going to discuss a serious matter that affects millions of seniors around the world: falls. I feel deeply about this because falls are not only common but also can lead to severe consequences for our loved ones. That’s why I believe in the importance of preventing falls in the elderly.
One in four Americans aged 65+ falls each year, making it a leading cause of injury among seniors. But the good news is that falls are preventable. Using my experiences, extensive research, and interactions with health professionals, I will share essential tips for preventing falls in 2023.
We’ll look at the reasons behind these falls, how to create safer environments, and how to boost physical fitness to increase balance and strength. So, let’s work together to protect our seniors from this preventable hazard.
Preventing Falls in The Elderly: Symptoms of Head Injury in Elderly
Head injuries in elderly patients can have serious consequences and it is important to be aware of the symptoms that may indicate a head injury. The symptoms of a head injury in elderly patients can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but some common symptoms to look out for include:
1. Headache
A persistent or worsening headache after a fall or head injury can be a sign of a more serious injury. It is important to monitor the intensity and duration of the headache.
2. Dizziness or loss of balance:
Elderly patients who experience dizziness or have difficulty maintaining their balance after a fall should be evaluated for a possible head injury.
3. Confusion or disorientation:
Confusion, memory loss, or difficulty concentrating can be signs of a head injury. If an elderly patient is having trouble remembering recent events or seems disoriented, it is important to seek medical attention.
4. Nausea or vomiting:
These symptoms can occur after a head injury and may indicate a more severe injury. If an elderly patient experiences persistent nausea or vomiting after a fall, it is important to seek medical attention.
5. Changes in vision or hearing:
Blurred vision, double vision, or ringing in the ears can be signs of a head injury. These symptoms should not be ignored and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
6. Mood changes or personality changes:
A head injury can sometimes cause changes in mood or behavior. If an elderly patient becomes irritable, agitated, or exhibits unusual behavior after a fall, it is important to seek medical attention.
It is important to note that these symptoms may not always be immediately apparent after a fall or head injury. Some symptoms may develop gradually over time, so it is important to monitor the elderly patient closely and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure the best possible outcome for the patient.
Treatment Options for Head Injuries in Elderly Patients
When an elderly patient falls and hits their head, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Head injuries can be serious and require prompt treatment to prevent further complications. The treatment options for head injuries in elderly patients may vary depending on the severity of the injury and the specific needs of the patient.
In mild cases, where there is no loss of consciousness or only a brief loss of consciousness, the primary treatment approach may involve observation and monitoring. The patient will be closely monitored for any changes in symptoms or signs of worsening. Pain management may be provided, and the patient may be advised to rest and avoid activities that could exacerbate the injury.
For moderate to severe head injuries, more intensive treatment may be necessary. This can include imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, to assess the extent of the injury and identify any underlying complications, such as bleeding or swelling in the brain. In some cases, surgery may be required to relieve pressure on the brain or repair any damage.
Medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent further complications. These can include pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and medications to control seizures or reduce swelling in the brain. The patient may also be advised to avoid certain activities or medications that could increase the risk of bleeding or further injury.
In addition to medical treatment, rehabilitation and recovery are essential for elderly patients with head injuries. This can involve physical therapy to regain strength and mobility, occupational therapy to improve daily living skills, and speech therapy to address any communication or swallowing difficulties. The rehabilitation process may be tailored to the specific needs and abilities of the patient, and it may take time for the patient to fully recover.
It is important for caregivers and family members to provide support and assistance during the treatment and recovery process. This can include helping with daily activities, ensuring a safe and supportive environment, and encouraging the patient to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Overall, the treatment options for head injuries in elderly patients are multifaceted and may involve a combination of medical interventions, rehabilitation, and support from caregivers. Prompt medical attention and ongoing care are crucial for ensuring the best possible outcomes for elderly patients who have experienced a head injury.
Preventing Falls in Elderly Patients: Essential Tips for 2023

Falls are a common occurrence among elderly patients and can lead to serious head injuries. It is crucial to take proactive measures to prevent falls and ensure the safety of elderly individuals. Here are some essential tips for preventing falls in elderly patients in 2023.
1. Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve strength, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls. Encourage elderly patients to participate in exercises such as walking, tai chi, or yoga, tailored to their abilities and preferences.
2. Home Modifications:
Assess the home environment for potential hazards and make necessary modifications. Install grab bars in bathrooms, ensure proper lighting in all areas, remove tripping hazards such as loose rugs or clutter, and secure handrails on staircases.
3. Medication Review:
Certain medications can cause dizziness or drowsiness, increasing the risk of falls. Regularly review the medications of elderly patients with their healthcare provider and discuss any potential side effects that may affect balance or coordination.
4. Vision and Hearing Check-ups:
Poor vision or hearing can contribute to falls. Schedule regular check-ups with an optometrist and audiologist to ensure that elderly patients have the appropriate corrective measures in place.
5. Footwear:
Encourage elderly patients to wear well-fitting, supportive footwear with non-slip soles. Avoid high heels or shoes with smooth bottoms that can increase the risk of slipping.
6. Assistive Devices:
Depending on the individual’s needs, consider the use of assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs to provide stability and support during mobility.
7. Fall Alarms and Monitoring Systems:
Install fall alarms or monitoring systems in the home to alert caregivers or healthcare providers in case of a fall. These devices can provide immediate assistance and reduce the time it takes to seek medical attention.
8. Regular Eye Exams:
Regular eye exams can detect vision problems that may contribute to falls. Encourage elderly patients to schedule eye exams at least once a year or as recommended by their eye care professional.
9. Stay Hydrated:
Dehydration can lead to dizziness and weakness, increasing the risk of falls. Ensure that elderly patients are drinking enough fluids throughout the day to maintain proper hydration.
10. Education and Awareness:
Educate elderly patients and their caregivers about fall prevention strategies and the importance of maintaining a safe environment. Raise awareness about the potential risks and consequences of falls
When to Seek Medical Attention after a Fall and Head Injury in Elderly Patients

When an elderly patient falls and hits their head, it is important to know when to seek medical attention. Head injuries can range from mild to severe, and prompt medical evaluation is crucial to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
One of the first signs that medical attention is needed is if the elderly patient loses consciousness, even if it is only for a brief moment. This could indicate a more serious head injury, such as a concussion or a brain bleed. Other symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention include severe headache, confusion, dizziness, vomiting, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, weakness or numbness in the limbs, and changes in vision.
It is also important to seek medical attention if the elderly patient is on blood thinners or has a bleeding disorder, as head injuries can lead to internal bleeding that may not be immediately apparent. Additionally, if the fall was from a significant height or involved a high-impact force, it is important to have the patient evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Even if the symptoms seem mild initially, it is still recommended to seek medical attention. Some head injuries may not present immediate symptoms but can worsen over time. A healthcare professional will be able to assess the severity of the injury and determine the appropriate course of action.
When seeking medical attention, it is important to provide the healthcare professional with as much information as possible about the fall and the symptoms experienced. This will help them make an accurate diagnosis and determine the best treatment plan. They may order imaging tests, such as a CT scan or an MRI, to further evaluate the head injury.
In conclusion, it is crucial to seek medical attention after an elderly patient falls and hits their head. Prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional can help determine the severity of the head injury and ensure appropriate treatment. It is better to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention, even if the symptoms initially seem mild. Remember, the health and well-being of the elderly patient should always be the top priority.
Complications and Long-Term Effects of Head Injuries in Elderly Patients
Head injuries in elderly patients can have significant complications and long-term effects. It is important to understand these potential outcomes in order to provide appropriate care and support for the patient.
One of the most common complications of head injuries in elderly patients is a traumatic brain injury (TBI). TBIs can range from mild concussions to severe brain damage. Symptoms of a TBI can include headaches, dizziness, confusion, memory problems, and changes in mood or behavior. In some cases, TBIs can lead to long-term cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with memory, attention, and problem-solving.
Another potential complication of head injuries in elderly patients is a subdural hematoma. This occurs when blood collects between the brain and the skull, putting pressure on the brain. Symptoms of a subdural hematoma can include headaches, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty speaking or moving. If left untreated, a subdural hematoma can be life-threatening.
In addition to these immediate complications, head injuries in elderly patients can also have long-term effects on their overall health and well-being. For example, a fall and head injury can lead to a loss of mobility and independence. Elderly patients may become fearful of falling again, leading to decreased physical activity and muscle weakness. This can further increase their risk of falls and injuries.
Furthermore, head injuries can also have psychological effects on elderly patients. They may experience anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a result of the traumatic event. These mental health issues can impact their quality of life and ability to engage in daily activities.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals and caregivers to closely monitor elderly patients who have experienced a head injury. Regular follow-up appointments and assessments can help identify any complications or long-term effects early on. Rehabilitation programs, including physical therapy and cognitive therapy, may be recommended to help the patient regain function and improve their overall well-being.
In conclusion, head injuries in elderly patients can have significant complications and long-term effects. It is important to be aware of these potential outcomes and provide appropriate care and support to minimize their impact. Regular monitoring, rehabilitation programs, and addressing any psychological effects are essential in promoting the recovery and well-being of elderly patients after a head injury.
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process for Elderly Patients after a Head Injury

After a head injury, elderly patients often require a comprehensive rehabilitation and recovery process to regain their physical and cognitive abilities. This process typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, with healthcare professionals from various specialties working together to develop an individualized treatment plan.
The rehabilitation process for elderly patients after a head injury may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation. Physical therapy focuses on improving strength, balance, and coordination, which are often affected after a fall and head injury. Occupational therapy helps patients regain their independence in daily activities such as dressing, bathing, and cooking. Speech therapy is essential for patients who experience difficulties with speech and swallowing. Cognitive rehabilitation aims to improve cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
The duration and intensity of rehabilitation will vary depending on the severity of the head injury and the individual’s overall health. Some patients may require inpatient rehabilitation in a specialized facility, while others may receive outpatient therapy or home-based rehabilitation. The rehabilitation team will closely monitor the patient’s progress and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
In addition to formal therapy sessions, elderly patients may also benefit from lifestyle modifications and assistive devices to support their recovery. This may include implementing safety measures at home, such as removing tripping hazards and installing grab bars in the bathroom. Assistive devices like walkers or canes can help improve mobility and prevent falls during the recovery process.
It is important for caregivers and family members to provide emotional support and encouragement throughout the rehabilitation and recovery process. Elderly patients may experience frustration or depression as they navigate the challenges of recovery. By offering reassurance and participating in therapy sessions, caregivers can play a crucial role in promoting the patient’s motivation and overall well-being.
Overall, the rehabilitation and recovery process for elderly patients after a head injury requires a comprehensive and individualized approach. With the right support and resources, many elderly patients can regain their independence and quality of life following a head injury.
Home Safety Tips for Elderly Patients to Prevent Falls and Head Injuries
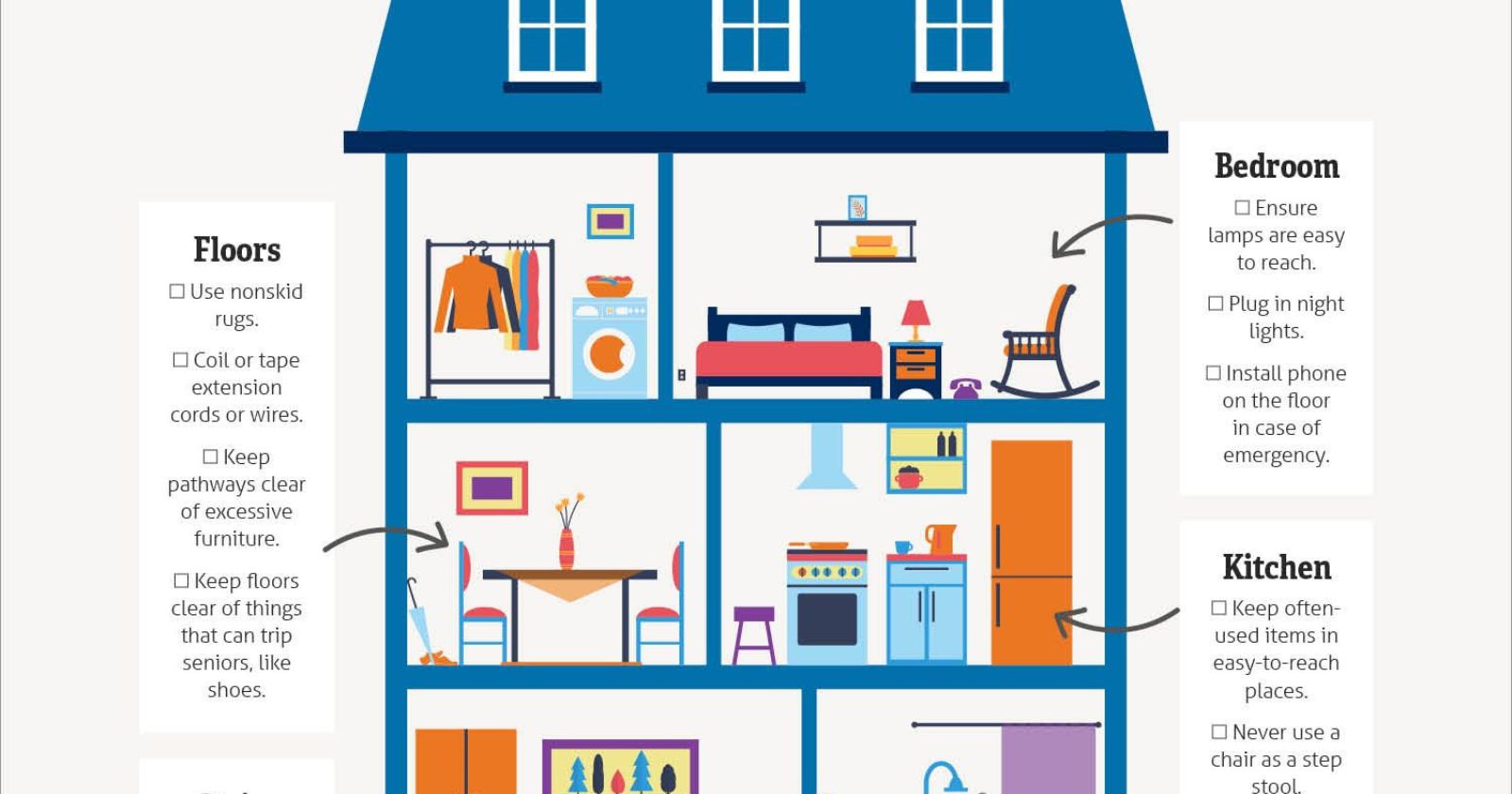

As we age, our risk of falling and sustaining head injuries increases. It is important for elderly patients and their caregivers to take proactive measures to create a safe home environment that minimizes the risk of falls and head injuries. Here are some essential home safety tips for elderly patients:
1. Remove tripping hazards:
Clear pathways of any clutter, such as loose rugs, electrical cords, or furniture that obstructs movement. Secure carpets and rugs with non-slip backing or double-sided tape.
2. Adequate lighting:
Ensure that all areas of the home are well-lit, especially stairways, hallways, and entrances. Install nightlights in bedrooms, bathrooms, and hallways to prevent falls during nighttime.
3. Grab bars and handrails:
Install grab bars in bathrooms near toilets, showers, and bathtubs to provide support and stability. Handrails should be installed on both sides of staircases to assist with balance while going up and down.
4. Non-slip surfaces:
Use non-slip mats or adhesive strips in the bathroom to prevent slipping on wet surfaces. Consider using non-slip pads under rugs or carpets to prevent them from sliding.
5. Proper footwear:
Encourage elderly patients to wear well-fitting, supportive shoes with non-slip soles both indoors and outdoors. Avoid walking in socks or slippers, as they can increase the risk of slipping.
6. Assistive devices:
If necessary, provide elderly patients with assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs to improve stability and mobility.
7. Bathroom safety:
Install raised toilet seats and bath benches to make it easier for elderly patients to sit and stand. Use a shower chair or handheld showerhead for added safety during bathing.
8. Medication management:
Ensure that medications are properly organized and stored in a way that minimizes the risk of falls. Consider using pill organizers or reminder systems to prevent medication errors.
9. Regular exercise:
Encourage elderly patients to engage in regular exercise programs that focus on strength, balance, and flexibility. This can help improve muscle strength and coordination, reducing the risk of falls.
10. Regular check-ups:
Schedule regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor any underlying medical conditions that may increase the risk of falls. Medications should also be reviewed periodically for potential side effects that may affect balance or coordination.
By implementing these home safety tips, elderly patients can significantly reduce
Risk Factors for Falls and Head Injuries in Elderly Patients

As individuals age, their risk of experiencing falls and head injuries increases. Understanding the risk factors associated with these incidents is crucial in order to prevent them and ensure the safety of elderly patients. Here are some common risk factors for falls and head injuries in elderly patients:
1. Age:
The risk of falls and head injuries tends to increase with age. Older adults may experience changes in balance, coordination, and vision, making them more susceptible to accidents.
2. Chronic health conditions:
Certain chronic health conditions, such as arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia, can increase the risk of falls and head injuries. These conditions may affect mobility, balance, and cognitive function, making it more difficult for elderly patients to navigate their surroundings safely.
3. Medications:
Some medications, particularly those used to treat conditions like high blood pressure, depression, and sleep disorders, can cause dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired coordination. These side effects can increase the risk of falls and head injuries.
4. Environmental hazards:
Poorly lit areas, uneven surfaces, loose rugs, cluttered spaces, and lack of handrails or grab bars can all contribute to falls and head injuries. It is important to ensure that the living environment of elderly patients is free from potential hazards.
5. Muscle weakness and balance problems:
Age-related muscle loss and decreased flexibility can lead to weakness and balance problems, increasing the risk of falls. Regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve strength and balance in elderly patients.
6. Vision and hearing impairments:
Poor vision and hearing can affect an individual’s ability to detect potential hazards and react appropriately. Regular eye and hearing exams are essential for maintaining optimal sensory function.
7. History of previous falls:
Elderly patients who have previously experienced falls are at a higher risk of falling again. Identifying the underlying causes of previous falls and implementing appropriate preventive measures is crucial in reducing the risk of future incidents.
By understanding these risk factors, healthcare professionals and caregivers can take proactive measures to prevent falls and head injuries in elderly patients. This may include modifying the living environment, reviewing medications, implementing exercise programs, and providing assistive devices. Regular assessments and monitoring can help identify any changes in risk factors and allow for timely interventions to ensure the safety and well-being of elderly patients.
Support and Resources Available for Caregivers of Elderly Patients with Head Injuries

Caring for an elderly patient with a head injury can be challenging and overwhelming for caregivers. It is important for caregivers to have access to support and resources to ensure the best possible care for their loved ones. Here are some support and resources available for caregivers of elderly patients with head injuries:
1. Support groups:
Joining a support group specifically for caregivers of elderly patients with head injuries can provide a valuable source of emotional support and practical advice. These groups often meet regularly and allow caregivers to share their experiences, learn from others, and receive guidance from professionals.
2. Caregiver training programs:
Many organizations offer caregiver training programs that provide education and skills development for caregivers. These programs can teach caregivers how to properly care for their loved ones, manage medications, and handle emergency situations.
3. Respite care services:
Taking care of an elderly patient with a head injury can be physically and emotionally exhausting. Respite care services provide temporary relief for caregivers by offering professional care for their loved ones. This allows caregivers to take a break, rest, and recharge.
4. Home healthcare services:
In some cases, caregivers may need assistance from healthcare professionals to provide specialized care for their loved ones. Home healthcare services can provide skilled nursing care, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other medical services in the comfort of the patient’s home.
5. Online resources:
The internet is a valuable tool for caregivers, providing access to a wealth of information and resources. There are numerous websites, forums, and online communities dedicated to caregiving, where caregivers can find information, ask questions, and connect with others in similar situations.
6. Caregiver support programs:
Many hospitals and healthcare organizations offer caregiver support programs that provide resources, education, and assistance to caregivers. These programs may include counseling services, educational workshops, and support groups.
7. Financial assistance:
Caring for an elderly patient with a head injury can be financially burdensome. There are various financial assistance programs available for caregivers, such as government-funded programs, insurance coverage, and grants. Caregivers should explore these options to alleviate some of the financial stress.
In conclusion, caregivers of elderly patients with head injuries need support and resources to ensure the best possible care for their loved ones. Support groups, caregiver training programs, respite care services, home healthcare services, online resources, caregiver support programs, and financial assistance are all valuable resources that can help caregivers navigate the challenges
Medical Tests and Evaluations for Diagnosing Head Injuries in Elderly Patients
When an elderly patient falls and hits their head, it is crucial to assess the extent of their head injury. This involves conducting various medical tests and evaluations to accurately diagnose the injury and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Here are some common tests and evaluations used for diagnosing head injuries in elderly patients:
1. Physical Examination:
A thorough physical examination is the first step in assessing a head injury. The healthcare provider will check for any visible signs of injury, such as bruising, swelling, or bleeding. They will also evaluate the patient’s neurological function, including their level of consciousness, pupil size and reaction, and motor responses.
2. Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS):
The GCS is a widely used tool to assess the severity of a head injury. It measures the patient’s eye-opening response, verbal response, and motor response. The score ranges from 3 to 15, with a lower score indicating a more severe injury.
3. Imaging Tests:
Imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, are often performed to visualize the brain and detect any structural abnormalities or bleeding. CT scans are particularly useful for identifying acute bleeding, while MRI scans provide more detailed information about the brain’s soft tissues.
4. Blood Tests:
Blood tests may be conducted to evaluate the patient’s overall health and rule out any underlying medical conditions that could contribute to the head injury. These tests can include a complete blood count (CBC), coagulation studies, and blood chemistry panels.
5. Neurological Assessments:
Neurological assessments, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) or Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), may be administered to assess the patient’s cognitive function and detect any changes or deficits caused by the head injury.
6. Electroencephalogram (EEG):
An EEG measures the electrical activity of the brain and can help identify any abnormal brain wave patterns that may indicate a brain injury or seizure activity.
7. Lumbar Puncture:
In some cases, a lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, may be performed to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid for signs of infection or bleeding.
It is important to note that the specific tests and evaluations conducted will depend on the individual patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the severity of the head injury. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan and ensuring the best possible outcome for elderly patients
Frequently Asked Questions
How can we prevent falling in the elderly?
Preventing falls in the elderly involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses various risk factors. Some key strategies include:
Regular Exercise: Engaging in strength and balance exercises can improve muscle strength and coordination, reducing the risk of falls.
Medication Management: Reviewing medications with a healthcare professional to identify and address drugs that may cause dizziness or imbalance.
Vision Check: Regular eye exams to detect and correct any vision issues that could contribute to falls.
Home Safety: Making modifications to the home environment, such as removing tripping hazards, installing handrails, and improving lighting, to reduce the risk of falls.
Footwear: Wearing properly fitting and supportive footwear to improve stability and prevent slips.
What are the 4 P’s of fall prevention?
The 4 P’s of fall prevention are a simple way to remember the key areas of focus for preventing falls in the elderly:
Plan: Encourage older adults to plan their activities, especially if they involve physical exertion or potential fall hazards.
Prepare: Ensure that the environment is prepared for safety, such as removing tripping hazards and using assistive devices if necessary.
Proceed with Caution: Encourage seniors to proceed with caution when moving around, being mindful of their surroundings and any potential hazards.
Prevent: Take proactive steps to prevent falls through regular exercise, medication management, and other preventive measures.
What is the most effective intervention to reduce falls in the elderly?
There isn’t a single intervention that is universally most effective in reducing falls in the elderly. Fall prevention is most successful when approached comprehensively, combining multiple strategies. However, exercise programs specifically targeting strength and balance have been shown to be highly effective in reducing falls in the elderly.
What are three interventions to prevent falls?
Three effective interventions to prevent falls in the elderly are:
Exercise Programs: Implementing regular strength and balance exercises to improve muscle strength and coordination.
Home Modifications: Making changes to the home environment to reduce fall hazards, such as removing clutter and installing grab bars and handrails.
Medication Management: Reviewing and adjusting medications to minimize side effects that may increase the risk of falls.
Other Places For You To Explore
Explore
Conclusion
As we conclude this discussion on preventing falls in the elderly, I sincerely hope you found these tips useful and informative. Please remember that each step we take towards preventing falls contributes significantly to improving the quality of life and maintaining the independence of our seniors.
With Elderly Independence, my goal is to offer guidance based on my experiences, the latest research, and advice from healthcare professionals. I strive to provide accurate, valuable, and reliable information that you can put into practice.
If you need further advice on preventing falls or any other aspect of senior care, I’m here to help. Together, we can make the journey of aging safer and more enjoyable for our loved ones.